In today’s digital-first world, cyber threats have grown more sophisticated, targeting users, devices, and networks across distributed environments. To counter these evolving risks, organizations in 2026 increasingly adopt the zero trust security model, a modern approach that assumes no user or system is inherently trustworthy. Unlike traditional perimeter-based defenses, this cybersecurity framework verifies every access request continuously, regardless of location or network. As remote work, cloud computing, and interconnected systems expand, the security strategy behind zero trust has become essential for protecting sensitive data and digital infrastructure.
The principle behind the zero trust security model is straightforward: never trust, always verify. Every user, device, and application must authenticate and prove authorization before accessing resources. This cybersecurity framework eliminates implicit trust that attackers often exploit in conventional networks. By enforcing strict identity verification, least-privilege access, and continuous monitoring, the security strategy ensures that even if a breach occurs, its impact remains limited. In 2026, zero trust is widely recognized as the most effective approach for safeguarding modern digital ecosystems.
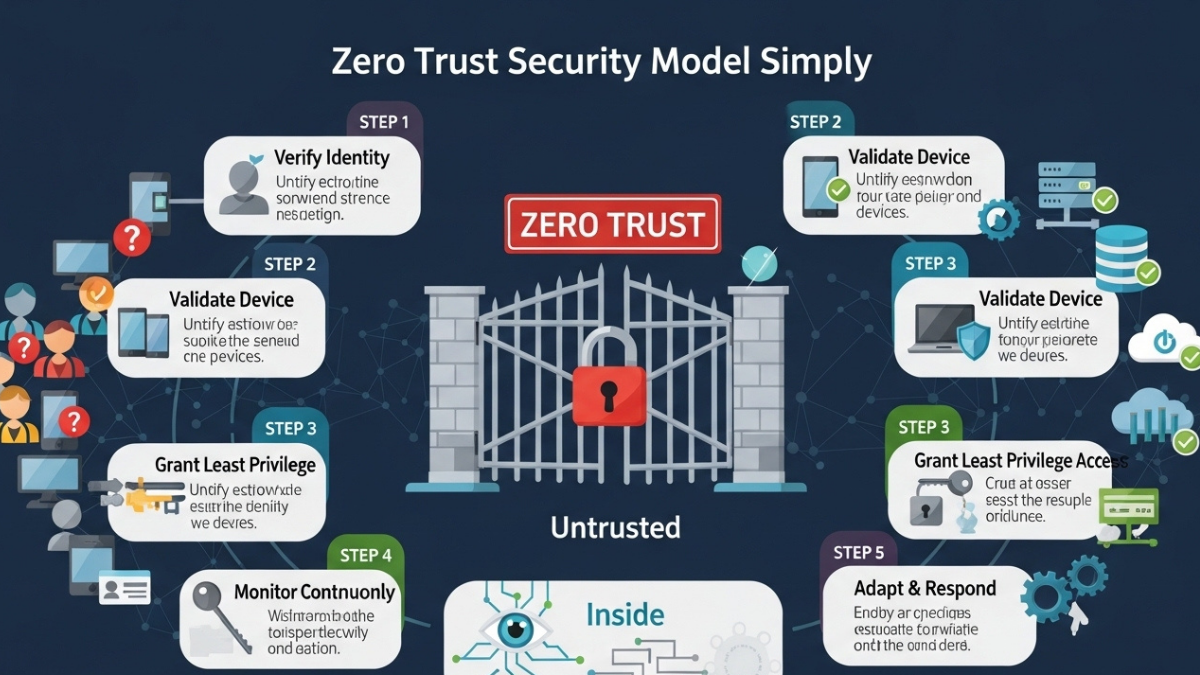
Core Principles of the Zero Trust Security Model
The effectiveness of the zero trust security model relies on several foundational principles that redefine how access and security are managed. This cybersecurity framework emphasizes verification, segmentation, and monitoring across all systems. Organizations implement these principles as part of a comprehensive security strategy.
Key principles include:
- Verify identity for every access request
- Enforce least-privilege permissions
- Assume breach mentality
- Segment networks and resources
- Monitor activity continuously
- Protect data at all layers
These principles ensure the zero trust security model minimizes risk exposure. By integrating them into a cybersecurity framework, organizations strengthen their overall security strategy against modern threats.
How Zero Trust Differs from Traditional Security
Traditional network security relied heavily on perimeter defenses, assuming internal users were trustworthy. The zero trust security model replaces this assumption with constant verification. This shift makes the cybersecurity framework more suitable for cloud, remote, and hybrid environments. As part of a modern security strategy, zero trust protects distributed systems more effectively.
| Security Aspect | Traditional security | Zero trust security model |
|---|---|---|
| Trust assumption | Internal users trusted | No implicit trust |
| Access control | Network-based | Identity-based |
| Monitoring | Perimeter-focused | Continuous |
| Network structure | Flat internal network | Segmented |
| Threat response | After detection | Preventive |
| Environment fit | On-premise | Cloud and hybrid |
These differences highlight why the zero trust security model is central to modern cybersecurity. The identity-driven cybersecurity framework aligns with evolving infrastructure, strengthening organizational security strategy.
Benefits of Zero Trust Cybersecurity Framework
The adoption of the zero trust security model provides measurable improvements in data protection and risk management. By removing implicit trust, this cybersecurity framework reduces attack surfaces and limits breach impact. Organizations implementing zero trust strengthen their overall security strategy across digital environments.
Major benefits include:
- Reduced risk of unauthorized access
- Contained impact of breaches
- Stronger protection for remote access
- Enhanced visibility into user activity
- Improved compliance and governance
- Adaptability to cloud environments
These advantages demonstrate why the zero trust security model is widely adopted in 2026. The layered cybersecurity framework ensures consistent enforcement of policies across the entire security strategy.
Implementing Zero Trust as a Security Strategy
Implementing the zero trust security model requires integrating technologies, policies, and processes into a unified security strategy. Organizations adopt identity management, device verification, and network segmentation within their cybersecurity framework to enforce trust boundaries.
Key implementation steps include:
- Deploying multi-factor authentication
- Implementing identity and access management
- Segmenting networks and applications
- Monitoring user and device behavior
- Encrypting data in transit and at rest
- Applying least-privilege access policies
These steps operationalize the zero trust security model across digital environments. By embedding zero trust principles into the cybersecurity framework, organizations create resilient and adaptive security strategy architectures.
Future of the Zero Trust Security Model
As cyber threats evolve, the zero trust security model will continue expanding across industries and technologies. In 2026 and beyond, AI-driven analytics and automation enhance the cybersecurity framework supporting zero trust. This evolution ensures the security strategy remains effective in increasingly complex digital ecosystems.
Emerging trends include:
- AI-based threat detection and response
- Continuous adaptive authentication
- Zero trust for IoT and edge devices
- Automated policy enforcement
- Integrated cloud-native zero trust platforms
These developments indicate that the zero trust security model will remain foundational for cybersecurity. As organizations adopt advanced cybersecurity framework technologies, zero trust will define future security strategy standards.
Conclusion
In 2026, the zero trust security model represents a fundamental shift in how organizations protect digital assets and data. By eliminating implicit trust and verifying every access request, this modern cybersecurity framework addresses the realities of cloud computing, remote work, and distributed systems. Implementing zero trust strengthens organizational security strategy, reducing breach risks and improving resilience. As digital ecosystems continue expanding, the zero trust security model will remain the cornerstone of effective cybersecurity in an increasingly interconnected world.
FAQs
What is the zero trust security model?
The zero trust security model is a cybersecurity approach that requires continuous verification of all users and devices before granting access.
Why is zero trust better than traditional security?
Unlike perimeter-based security, zero trust assumes no implicit trust, making it more effective for modern cloud and remote environments.
What is a cybersecurity framework?
A cybersecurity framework is a structured approach to managing and protecting digital systems and data from threats.
How does zero trust improve security strategy?
Zero trust limits access, monitors activity continuously, and reduces breach impact, strengthening overall security strategy.
Is zero trust used in cloud environments?
Yes, the zero trust security model is especially effective for cloud and hybrid infrastructures.
Click here to learn more